what are the nlp techniques that can help us in our lives?

what are the NLP techniques that can help us in our lives?
Richard Bandler and John Grinder started a study about the most influential people in understanding people to create the Neuro-Linguistic Programming, or NLP, techniques. They have studied the most successful therapies and therapists to understand their patterns of communication, behavior, and understanding. Today, obtaining an NLP certification to become an NLP life coach is a great way to use the NLP modeling techniques to help others.
NLP techniques organize the best strategies for personal development with a practice and experience-based focus. This is one of the techniques that the founder of YOGI TIMES and relationship NLP life coach Sophie Parienti uses to help you understand your relationships and their challenges by focusing on resolution and compassion instead of conflicts.
Since we are born, we start to receive stimuli through our senses; all these go through our neurological system. NLP modeling is about being aware of this bank of data, we can call it learning or programming, which determines our thoughts, actions, and feelings. Unfortunately, most of this information in the unconscious mind, since humans only use their intellect at 5 percent, so we miss a lot of our knowledge that we could otherwise explore with the right NLP certification tools and training.
Assumptions of NLP techniques
- Everyone has their own ¨Map¨ of reality.
- The map is not the actual territory.
- It is not the reality that limits us but our map of it.
- On a system, the element most flexible and with more alternatives is who wins the system.
- Failure doesn’t exist; rather, its results are something that we can learn from.
- If what we do does not work, let’s make it different.
- Behavior is not the same as identity.
- People always try their best, with a positive and adaptive attitude.
- People already have all their needed resources.
NLP modeling exercise by learning to listen (Calibration)
What is listening?
It is important to have an NLP certification because sometimes, as an NLP life coach, before listening to someone, we assume many things from our experiences, which generally have nothing to do with their expertise. As a result, we try to understand the other person’s perspective from our map, making the other person feel like they do not understand the conversation. So now we know that listening is not about interpreting what is going on.
What should we pay attention to in NLP modeling?
When you listen, you don’t add or eliminate anything. All your attention is on the person in front of you, and you take what is observable through your senses. So for example, if you take or add something, we say that you are interpreting and that you will probably be wrong, and can’t communicate with the person you are talking to.
What does active listening mean?
In a proper training of NLP certification, we use active listening to help us understand the internal experience of the person we are talking to. Our backgrounds are visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, or tactile. These experiences can have an origin from the outside, for example, a picture we saw on the wall or an internal source when we remember about an image.
The exciting thing about NLP techniques is that we can get all this information by only paying attention to what is in front of us. The most important thing is not about the content that the person explains, but what happens to the person while they live that experience.
NLP life coach: what kind of internal experience is the person I am talking to having?
As NLP life coaches, we can find the first place on the predicates of the phrase, for example:
“There is something that worries me, or I do not see it.” When someone says “I am feeling worried, and I can see a blurry image that doesn’t let me see¨, this happens in our unconscious mind most of the time, and we aren’t aware of it.
In NLP modeling, we pay attention to these predicates to find the words that define their internal experience through visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, or tactile. What a person says is a literal transcription of what he is living internally at that moment. What happens is that experience goes fast, one after the other, and most of the time, we are not aware of what is happening. It helps us tune with the person.
Pay attention to corporal language with NLP techniques
We can also pay attention to corporal language to see what’s going out inside of a person. In NLP techniques, all gestures that a person makes while speaking refer to specific contents of the internal experiences that they have at that moment. So, for example, if someone faces their hands and leaves a space while talking about how big the rock was, he is visualizing that rock.
Another indicator we learn during NLP certification training can be their posture, look, breathing rhythm, or skin tone while speaking, for example. Usually, when a person looks for internal information, he looks up; if it is something that he wants to remember, it goes up and right, but is it something he wants to imagine, it goes up and left. He is looking for auditive material; he will look to the right or left depending on if he is trying to remember or imagine.
Finally, suppose he is looking to recall an olfactory, taste, or tactile (kinesthetic) experience. He will look down and left in that case, and there is a very particular material called internal dialogue that usually people look down and right. It is not always like this; some people have an inverse process, the important thing is to find out how the person works. This is how this NLP modeling exercise works:
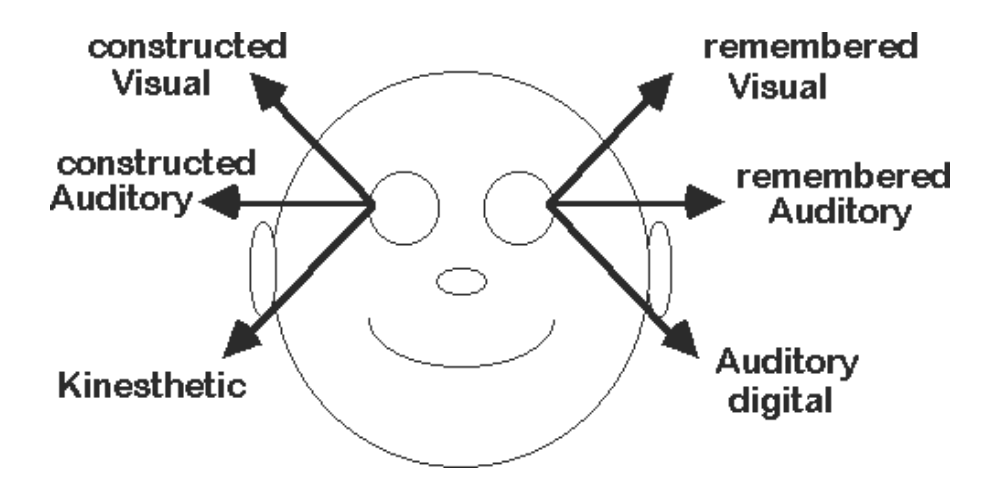
As an NLP life coach, we can also observe that most people have a preferred channel to use: the visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, or tactile. We can use this table to find it, but as before, this is not a mathematical formula. Still, you can observe that, for example, when people talk about their experiences and focus on their internal sensations, the volume and speed of their words go down. This is the representation of these NLP techniques:
| Volum | Speed | |
| Visual | High | High |
| Auditive | Medium | Medium |
| Kinesthetic | Low | Low |
Also, Read >>> Yoga Certification Online
Connect with the other with NLP techniques (Rapport)
NLP life coach concept: What is Rapport?
Rapport is defined as a condition of receptivity in NLP techniques. The individual or people you’re talking with are responsive to you, both consciously and subconsciously, and you, therefore, have the upper hand in the conversation. So is using a mirror strategy to connect with the other person.
How to get this NLP modeling exercise?
With training in NLP certification, you will learn to let the other person express what he is going through with his posture and adopt the same pose. Again, we gave the other person the perspective to see what is going on from the outside; this gives him an entirely new view of the situation.
It has an unblocked response from his neurology and is a starting point for moving things from the inside. To continue, you can express what you feel physically when you adopt his posture, then how you feel emotionally with this position and how you feel with the rest of the people.
How to use these NLP techniques and for what?
In this NLP modeling technique, we have to ask questions to help him find an exit door to his challenges. In the first place, you connect with the person adopting the same stance; then, he can see this experience from another point of view, which helps to see what this experience means to him.
Also Read>>> Complicated Relationship
With NLP techniques, we can connect with any other aspect of his behavior, like the tone of voice, the type of predicates used, the speed of diction, etc. Showing him how we perceive that posture or experience will give him another perspective to start looking for an exit door with new positions. Then we can make him repeat the sequence three times, so his neurology gets what he has to do every time he is in that situation.
Here is a real-world example of an NLP life coach in action: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rqhSWI4-hnA
With this NLP certification exercise, we connect with the person by putting ourselves at the same level through the use of empathy, listening, and copying his verbal or nonverbal communication. Until the other person is not entirely connected with us, we can not change our communication.
NLP modeling: connect with your internal state (Anchoring)

How do the mechanisms of association of ideas work in NLP life coach?
It is simple: the first is to know what we understand about ideas. One idea is an image, sound, sensation, or intern conversation; it also can be a combination of these. Second, we should know that ideas are not self-generated; they come from an association of idea goes after the other.
How can I associate a stimulus to a state?
NLP techniques define two events that are experienced together or close in time or space and tend to manifest together within us in the form of associated ideas. For example, if I misbehave, I might receive a slap, and the probability that when I misbehave again, I will remember the slap is very high.
As you can imagine, as you experience the associated event, the more will you live by that idea, and the connection between the two concepts will be like a stranger creating an “anchor.” Also, it relates to the intensity of the event as more intensity means more connection.
How can I associate a stimulus to a state? What is the use of doing these NLP techniques?
Ask yourself about a difficult situation you would like to change, and observe what you need to accomplish this situation. To apply these NLP techniques, we have to pay attention to how your posture changes when you imagine that citation; now, move to another place to help you disconnect from the other experience. Now, remember a situation when you have what you need now, observe how your physiology changes, pay attention to the images to intensify your connection with the case, and notice the sensation.
Where is it? Now with all this NLP modeling information, create an anchor that could be any posture or gesture. What will you call this sensation? Now that you have the visual and auditory anchor, come back to your problem situation. How does it feel now? We are changing our personal history for a new experience; in this way, the next time we have this “problem,” we will come up with a unique solution, “anchor” recording this in our neurology system.
Modifications of internal states with NLP techniques (Submodalities)
What are submodalities in NLP modeling?
Becoming an NLP life coach is like being a cinema director that clearly knows what they want to express in their film from different angles, light, sounds, etc. NLP techniques describe that the content is as important as the way of telling the story.
Curiously, the same thing happens with our internal images that generate our neurology and the sounds and sensations.
Visual: associated (from inside) or dissociated (from outside); if dissociated, from what perspective, panoramic or framed; if framed, in what position (centered or offset from the center); black and white or color; light or dark; clear or blurry; static or moving.
Auditory: with sound or without sound; high or low sound; of the direction of the sound, near or far; clear or noisy; high or low; continuous or not; fast or slow; the rhythm of sound.
Kinetic: are intense or soft sensations; location in the body; the texture of the feeling; constant or intermittent; the temperature of the sense; size, shape, pressure, and vibration.
What is their importance of NLP techniques?
In NLP techniques is essential to know that every combination of visual and auditory reactions gives us a kinesthetic sensation. Changing the submodalities, we change the meaning of the scene that it had for us before. It is essential to know that our neurology registers every situation in types or groups with common submodalities, which gives meaning to all of them.
How to modify internal states through work with NLP modeling submodalities?
As an NLP coach, think about three different situations in which you could have the same difficulties; you will know this because the internal sensation will be the same. Put your attention on the images and ask questions to know the details of these projections. Then, move to another space and imagine the second experience doing the same questions to learn more about the repeating pattern. Let’s go for the third and last situation with the same process.
What we have done until now is to see what NLP modeling submodalities we have in common. Now move to another space, and let’s change those NLP modeling submodalities to improve your difficult situations. Get a position when you feel you have all the resources you need to accomplish any case and observe the pattern as we did before.
Now observe the relations NLP modeling submodalities between the two different situations and apply them to the problem situations. This an essential training in NLP certification that to change your meaning of this situation is not a situation of “difficulty” anymore, now do it with your free everyday situations that we observed before. In one instant, we change the meaning of the situations you have as “difficult”, and you will see what happens the next time you go through this situation again.
From one state to another with NLP techniques (Motivation strategies)
How do we get motivated, and how do we get demotivated?
Before we start something “difficult,” we already unmotivate ourselves with phrases like “I have to do it.” So first, we need to know how we process the situation, see it, what sensation we get, and what we tell ourselves. Use NLP techniques now try to learn another strategy that can motivate you to do this “difficult” task: change the things you see, feel and say.
What is the neurological sequence in this process of NLP certification?
- Describe the unmotivated strategy.
- Create a new motivational plan with the same line of modalities sensations.
- Repeat this new strategy.
How to replace a demotivating sequence with a motivational one?
We know where our strategies come from with NLP certification and our neurology that organizes every experience in our senses. We usually are not conscious of these stimulus sequences because they go so fast one after another, but now you can stop observing them, evaluate them, and change them if you want.
NLP coach: Changing my perception (Re-label)
How do I see other people? What impact does it have on my relationship with them? How to see them in another way to be able to change my relationship?
How do I see other people with a NLP certification exercise?
From your perspective, imagine a difficult person to talk with and give him or her a name that defines their way of communicating with you. Now let’s remember that difficult conversation that you had with these people.
Where is your sensation? Now describe what they are doing with their behavior, explain it without trying to guess anything, just what you perceive through your senses. What is this person doing? Okay, after you finish describing the situation, move yourself to another part of the room. What positive thing is this person looking for?
Do you think that person fits with the determination you put on them? Now that you have a new perspective over them, what label will you give to them? Okay, now come back to your position before and the difficult conversation you had with them. How do you feel now? How can you change your relationship with this person directly that you put them on a different label?
What impact does it have on my relationship with this person?
- Identify the “label” that we have put on them.
- Describe observable behaviors.
- Imagine what good thing this person is looking for in themself with these behaviors.
- Put a new label on the person.
How can I see them in another way, so that I can be able to change my relationship?
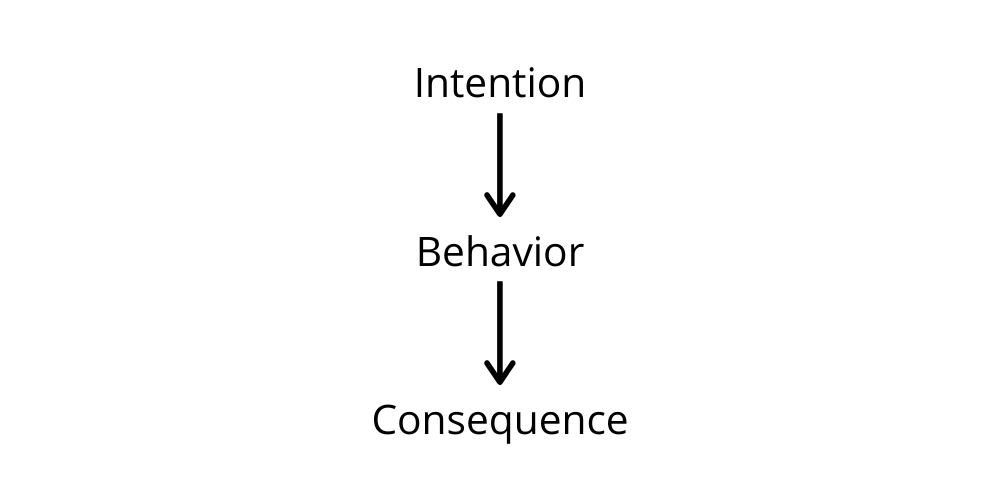
With NLP certification, we learn that every action humans do has a positive intention that will help us put ourselves in the shoes of other people and improve our relationship with them. We need to differentiate between the purpose and consequence of an action. Even if the effects were adverse, the intention is always positive for the one that is acting. This is the NLP coach representation:
Expanding my map with NLP techniques (Triple perceptual position)
How can I change my perspective of a conflict situation as an NLP life coach?
Set up space with three different points and start remembering a problematic situation with someone. What can you observe in the behavior? When you define the case objectively from your perspective, move to the other side and imagine that you are that person you were talking to. Same process now, what can you observe objectively now from this different perspective? After defining it, how do you feel? Hopefully good!
Now let’s move to a different part of the room to observe the situation from another perspective. Now that we see the problem from a distance, what do you see? What is the positive intention of both of them? What could you tell them to get out of this situation? Is there any other way of acting? Okay, we’ve almost got it.
Please come back to your initial position. How is it? What impact does it have? Now there is less importance on what is happening. With this NLP certification exercise, you get your power back now, so you can do something to manage the situation.
NLP coach: Congruences for change (Polarity integration)
What is logic? Are we congruent? How do I identify parts of myself that are not congruent? How do I integrate and align these parts?
As an NLP coach, think about a part of yourself that you would like to change. Now imagine the part of yourself that you would like to change in this part of the space. Tell the other part of you what you think about it. What would you like the other person to do? Move to the starting side and listen to what you say before. What do you want to speak to the other part? What positive intention are you looking for in the other part of you? Say it to them.
Come back to the other side and listen to what you said. What is your reply? Once you understand both parts of yourself, remove yourself to another part of the room where you can see both sides throughout the distance. Stay calm, relax your shoulders and back. Observe both sides. Now sit down straight and put the palm of your hands looking up.
Connect with yourself using NLP techniques
Focus your attention on these points. Now put the palms facing each other while closing them together little by little. Once they are both close, bring them to your chest. Take a deep breath and take your time.
The objective of this NLP certification exercise is to integrate both perspectives in our neurology. We usually are not congruent with ourselves. This is because humans are very complex; all our ideas, beliefs, values, etc., are learned in a determinate way, but also there are other things we learned in different ways, and that is where we find the conflict.
We usually choose one, and we always act in the same way even if it is not adequate for what we are looking to accomplish. We leave the other side entirely out of our attention, and we forget about it. This is about solving this conflict between both sides.
First, both sides need to express themselves by taking consciousness of both sides inside the person and seeing how both sides have a positive intention for themselves. Typically, this is great new information for the person because we usually think this limits us, but we realize it has a lot of sense.
Then we put ourselves out of the conversation when both sides manifest themselves; clearly, this helps us connect with both sides and create an ¨anchor¨. The importance is that the process occurs slowly in a subconscious way and brings both sides to yourself, enjoying the freedom that this brings to yourself.
NLP coach: Knowing myself more (subconscious concept)

NLP life coach: What is the subconscious?
A straightforward NLP certification exercise that helps us understand this is to put all our attention to one of the toes on our right foot. Now we can say we are conscious about the sensation in our right foot. What happened before we put the attention there? Our neurology is like our heart; always working, never resting. It is continuously receiving and generating images, sounds, words, and sensations.
What a significant amount of information! Not all the data has the same importance for us. Most of this information may be irrelevant, so we ignore it. While other details could be essential for us and we need to pay attention to it. Our attention focuses on the importance of all of this information while the rest lives under the subconscious mind.
NLP life coach: What is it?
For example, when we do something new, we need our conscious mind to do it and pay a lot of attention, but once we master this, we do it unconsciously. It is difficult to predict, but scientists say that more than 95 percent of our life experiences happen unconsciously.
NLP life coach: What is my subconscious looking for?
As an NLP coach, we know that all unconscious actions have a positive intention for us when our subconscious mind is programmed for something good. It is at our service, and the goal is to our survival and wellbeing even though some of our programmed behaviors are not adequate for specific moments, for example, when you drip snot in front of people. We can reprogram these specific behaviors if we are conscious about them for our personal goals in every situation.
Helping with questions with NLP techniques (Metamodel)
How important is the question? Should I pay attention to ask the question? What questions are helpful, and when? What is the language metamodel?
Like a video game, NLP certification material shows us how life is a game:
- We need to know the rules of the game to play it properly. We need to practice and experiment with everything to understand the game’s laws to get to the next level.
- Our mind can not see the real world, we see a map created by our mind, but a map is accurate enough to have some limits to the real world. The map could be good if it is helpful for the real world.
- The suffering comes when our map of the world stops being beneficial for the real world. Sometimes we get trapped in our map and forget that we need to learn something new to get to the next level.
Also, Read >>> Healy Energy Frequency Device Review.+
NLP modeling: language metamodel
NLP modeling: Generalizations
Unspecific verb: according to their meaning, the verbs may be more or less specific and evocative of a particular sensory experience; for example, it is not the same “expressing” as “gesturing” than “smile”; each one of you sees a different version of you. of concretion and connection with a concrete experience to reconnect the model of the world with the concrete sensory experiences, in the face of a non-specific verb we use questions of the type: in what way, specifically …?
Universal quantifiers: (“always,” “never” everything, “nothing, “everyone, “no one”). We use questions of this type. Are you telling me that there has been not a single time when? Or do we repeat the universal quantifier as a question, always, always, always? Never, never, ever?
Performative loss or judgment: expressing an opinion as a universal law known by everyone. Badly raising the tone of voice, they demonstrate that the person does not introduce another possibility other than that. They contain words of the type: good, bad, correct, incorrect, crazy, rope, moral, immoral. Of the judgment: who says that it is wrong to raise the tone of voice? So that the person realizes that it is an opinion of theirs more than an irrefutable fact.
NLP modeling: Eliminations
Lack of referential index: not clear what or who is the subject preached to help explore the experience, we use questions like who / what …?
Comparative omission: we detect by using adjectives or attributes of the type: best, worst, expensive, cheap, ‘complicated, wherein the background of what is being done is compared with something, but it is not specifying with what has established the comparison. We use questions of the type: better than what, precisely? More expensive, compared to what? Hard, compared to what?
Modal operators of possibility: they are generalizations that establish that something is not possible: “it cannot be …” “it is impossible …”,” I can’t do it.” We challenge them with questions of the type “what is preventing you?”, “what would happen if you did it?”
Necessary modal operators: these are generalizations that establish behavior rules as something essential and cannot be changed. For example, “I have to” “have,” “is necessary.” with questions of the type: “what if?”, “what if not?”.
Distortions in NLP certification
Cause-effect: a reaction by one person is considered a necessary consequence of the action of another person. example: “the noise that it makes when I chew makes me nervous.” Nobody can activate or activate the emotions or sensations of a person except for the person. How does the fact that I make noise necessarily imply that you should get nervous?
Complex equivalence: two different experiences are expressed as meaning the same or being equivalent: he doesn’t love me.” We challenge the person with questions of the type. How does not looking at you mean that they do not love you?
Mental reading: a person believes to know what another person thinks without someone having said it. We can challenge that belief with questions of the type: How do you know? How did you get to that conclusion? Also, use questions to question the cause-effect relationship (a is equivalent to b) that typically underlines this type of distortion: “if such a person does such a thing, it is because they think otherwise.” To do this, we question the cause-effect relationship by asking the person if they know or can imagine any situation.
Nominalizations: express in the form of a concluded event (substantive). It is not possible that something is a process in progress (verb) and over which we have control. A noun is a nominalization; if adding to it the words “in progress,” it still makes sense. For example: “Confusion makes it impossible to work.” To challenge nominalizations, we ask questions of the type: “how do you get confused?” or “what would happen if you are not confused? “
Assumptions: an assumption is an affirmation that has to be true for the saying to make sense. For example, in the saying: “close the door well when you leave home,” there are many assumptions: you are either home or going to leave your home; the house has a door; the door can close right or wrong. If any of these statements were not considered accurate by the expression, the phrase would not make sense.
How to help with NLP modeling?
As an NLP coach, put your attention on the other person, observe all the things you can from your senses. Instead, listen to your experiences and give people advice and ask them questions to think by themselves. If you give them your advice most of the time, it doesn’t work because you don’t see the big picture, but even if it works, you make them independent of themselves instead of giving them the freedom and ability to think by themselves.
Discovering what I want and what stops me with NLP techniques (Objectives and believes)

How do I connect with what I want as an NLP life coach? What’s stopping me, and how can I change it, and identify an outstanding goal for me?
One of the most used techniques for an NLP life coach is to set a goal and be aware of the directions. But most of the time, these are cognitive goals, for example, ¨I want to change my job¨or ¨I want a car¨. These goals are reasonable; what happens is that we don’t stay in that direction most of the time.
Everything is well planned, but I can not stay on the right path. Why does this happen? What could be happening with this goal? It could be incoherent between what we think and what we feel; it may be a belief that doesn’t let us go there. Even when we are conscious that we want to go there, we think that most of them are unconscious when we talk about ideas. So let’s organize it with this NLP certification exercise!
Close your eyes and stay in touch with your breathing. Now put your attention to your breathing. Most of the time, we breathe unconsciously, the NLP life coach program uses breathing to connect with our inner self and live consciously. Draw a circle between the points of your palm hands and the part of your body where you feel the breathing.
Once you connect with yourself with these NLP techniques, you enter a dimension of infinite possibilities because you have access to all your neurology information. Now ask yourself what your profound desire is. Close your eyes and immerse yourself in that sense, before bringing your attention back to the present.
NLP modeling: change your beliefs to change your life
Describe what you have seen, smell, or heard. You look well in that state; sometimes, it is not that important what we do or what we have because there is always a moment to be; the most crucial thing is from where you are acting. NLP certification exercises help you be in line with yourself to create an expression that is much deeper and meaningful to you. Are you feeling good now? If it feels so good, why don’t you have that now? Anwer with your body and observe what is going on.
We usually have five types of limiting beliefs:
- Is it a desirable goal?
- Possible to accomplish?
- Appropriate to the circumstances?
- Am I able to accomplish this goal?
- Do I deserve this goal?
The first thing we did to enter a trance mood with the triangle NLP certification exercise was to be aware of what happens inside us and ask ourselves, what is our deepest desire? Then we invite ourselves to live this desire, then the critical NLP coach question: if it is that good, why don’t you have it yet?
Determine then what is the limiting belief that stops you from getting your desired goal. Use these NLP techniques to investigate the origin of the idea, knowing that all behaviors have a positive intention, so you don’t judge yourself or others that cause you that limitation.



